Transpiration in plants takes place through stomata, tiny pores primarily located on the underside of leaves. These stomata are crucial for gas exchange, allowing carbon dioxide in for photosynthesis and releasing oxygen. However, this process also inevitably leads to water loss – transpiration. Understanding this process is key to appreciating how plants survive and thrive in various environments.
The Stomata: Gateways for Transpiration
Stomata are not just simple openings; they are complex structures controlled by guard cells. These guard cells regulate the opening and closing of the stomata, responding to environmental factors like light, temperature, and humidity. When conditions are favorable for photosynthesis, the guard cells swell, opening the stomata and allowing for gas exchange. This opening, however, also facilitates the escape of water vapor, driving transpiration.
How Environmental Factors Influence Transpiration
Several environmental factors influence the rate of transpiration. High temperatures increase the rate of evaporation, leading to increased transpiration. Similarly, low humidity creates a steeper concentration gradient between the leaf’s interior and the surrounding air, promoting water loss. Wind also plays a significant role by carrying away the humid air surrounding the leaf, further increasing the concentration gradient and driving transpiration. Conversely, high humidity and low temperatures reduce transpiration.
The Journey of Water: From Roots to Leaves
Water absorbed by the roots travels upwards through the xylem, a network of vessels within the plant stem, reaching the leaves. This upward movement is driven by a combination of factors, including root pressure and the cohesive and adhesive properties of water molecules. Once in the leaves, water evaporates from the mesophyll cells into the intercellular spaces and finally diffuses out through the open stomata.
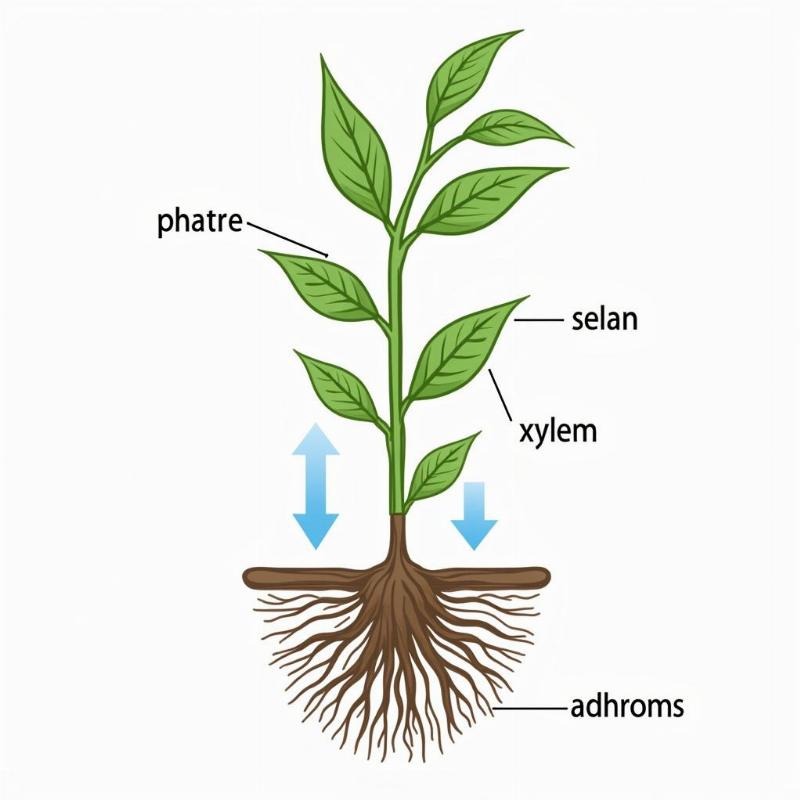 Water movement in plants
Water movement in plants
The Importance of Transpiration in Plant Survival
While transpiration leads to water loss, it is not simply a negative side effect. It plays several crucial roles in plant survival, including:
- Cooling: The evaporation of water during transpiration has a cooling effect on the leaves, preventing overheating, especially in hot and sunny conditions.
- Nutrient uptake: Transpiration creates a “pull” that helps draw water and dissolved nutrients from the soil up through the plant.
- Maintaining turgor pressure: Turgor pressure, the pressure exerted by water within plant cells, is essential for maintaining plant structure and supporting growth. Transpiration contributes to this pressure by ensuring a constant flow of water through the plant.
Transpiration and Climate: A Two-Way Street
Just as climate affects transpiration, so too does transpiration affect the local climate. Large forests, with their high rates of transpiration, release significant amounts of water vapor into the atmosphere, contributing to rainfall and influencing local weather patterns. This connection highlights the importance of preserving forests and understanding the intricate relationship between plants and their environment. how do forests influence the climate of a place
Conclusion
Transpiration in plants takes place through stomata, a process crucial for gas exchange, cooling, nutrient uptake, and maintaining turgor pressure. While environmental factors like temperature and humidity influence transpiration rates, the process itself contributes to local climate regulation. Understanding this intricate interplay between plants and their environment is essential for both botanical studies and environmental conservation efforts.
FAQ
- What are stomata? Stomata are tiny pores on the surface of leaves, primarily on the underside, that regulate gas exchange and transpiration.
- What are guard cells? Guard cells are specialized cells surrounding each stoma that control its opening and closing.
- How does transpiration cool plants? The evaporation of water during transpiration absorbs heat, having a cooling effect similar to sweating in humans.
- Why is transpiration important for nutrient uptake? Transpiration creates a pull that draws water and dissolved nutrients from the soil up through the plant.
- How does transpiration affect the local climate? Transpiration releases large amounts of water vapor into the atmosphere, influencing local humidity and rainfall patterns.
- What factors affect the rate of transpiration? Temperature, humidity, wind, and light intensity are key factors that influence transpiration rates.
- What is the role of xylem in transpiration? Xylem is the vascular tissue responsible for transporting water from the roots to the leaves for transpiration.
PlaTovi: Your Travel Companion
PlaTovi is your trusted partner for exploring India and beyond. We specialize in crafting unforgettable travel experiences, from traditional tour packages to bespoke itineraries tailored to your individual needs. Whether you’re seeking cultural immersion, adventure, or relaxation, PlaTovi can help you plan your perfect getaway. We offer comprehensive services including hotel and resort bookings, international and domestic flight ticketing, event planning, car rentals, and visa assistance. Contact us today to start planning your next adventure! Email: contact@places-to-visit.in, Phone: +91 22-2517-3581.